“There was a significant decrease in gambling, both land-based and online, during the lockdown due to the Covid19 pandemic restrictions, but there was a spike just after the relaxation of regulations, especially online gambling.” These are the first considerations at the end of the research coordinated by theIstituto Superiore di Sanità in collaboration with theMario Negri Institute, theInstitute for the Study, Prevention and Oncology Network (ISPRO), theUniversity of Pavia and theVita-Salute San Raffaele University of Milan.
The results
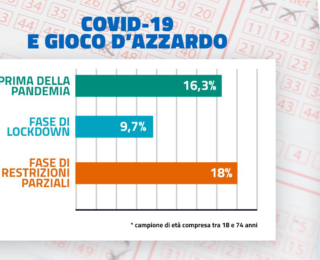
The practice of gambling from 16.3 percent in the pre-pandemic period dropped during the lockdown period to 9.7 percent and then rose again to 18 percent in the partial restriction period.
Land-based gambling declined from 9.9 percent in the pre-pandemic period to 2.4 percent in the lockdown period, and then recovered to 8 percent in the partial restriction period. Online gaming, on the other hand, increased from 10.0% in the pre-pandemic period to8% in the lockdown, rising to 13% in the period of partial restrictions.
During the lockdown, among players the median time spent playing increased by almost an hour. In addition, the1,1% started playing right in the period of total restriction, while the 19,7% of those who were already gambling increased their total gambling activity, and this happened most frequently to young people, smokers, cannabis users, and those who had risky alcohol consumption.
The most played games in all surveys are confirmed to be Scratch Card for land-based gambling and for online gambling Sports Betting, Scratch Card and Slot Machines.
The champion
The study involved a sample of the Italian population aged between 18 and 74 years old; the data collected are about playing habits during the lockdown period (April 27-May 3, 2020) compared with pre-pandemic habits and a subsequent phase of partial restrictions (November 27-December 20, 2020).
“With the loosening of restrictions,” says Roberta Pacifici, director of the National Center for Addiction and Doping, “there has been a new increase in the gambling population, to the point where, in the case of online gamblers, it exceeds the pre-pandemic percentage. The strong relationship found between situations of emotional distress and addictive behavior calls for urgent policies to prevent vulnerable populations from increasing and developing severe gambling addiction.”
Listen to Mario Calvagno and Carmen Zammataro’s interview on RVS Rome with Dr. Roberta Pacifici.